Our Projects
Cinturón Verde Restoration Project
Project Overview
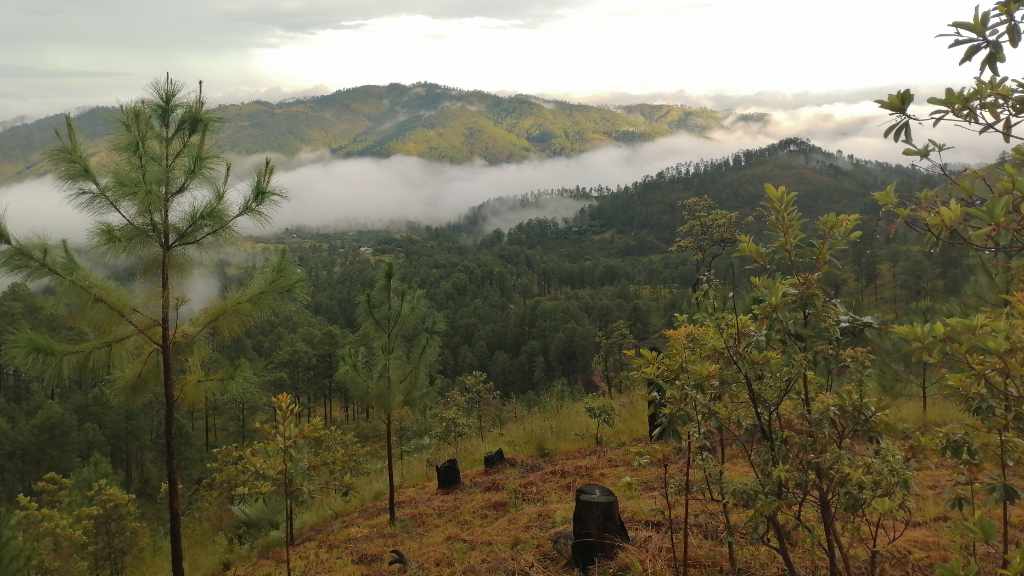
The Cinturón Verde Restoration Project represents Eden’s historic accomplishments in Honduras, demonstrating expertise now applicable to carbon-eligible landscapes. While implementation concluded in 2024, this innovative 96,500-hectare initiative successfully protected Tegucigalpa’s critical water resources by integrating five protected areas into a resilient green belt serving over one million residents.
The project’s greatest legacy lies in its advanced fire management systems, developed in response to severe 2024 fire impacts. These systems, along with successful restoration of landscape connectivity between cloud forests, pine-oak forests, and broadleaf ecosystems, proved essential for safeguarding water resources and biodiversity. By establishing strategic firebreaks, facilitating natural regeneration, and building strong community partnerships, Cinturón Verde provides valuable lessons for implementing fire-resilient carbon projects in similar landscapes.
Ecosystem
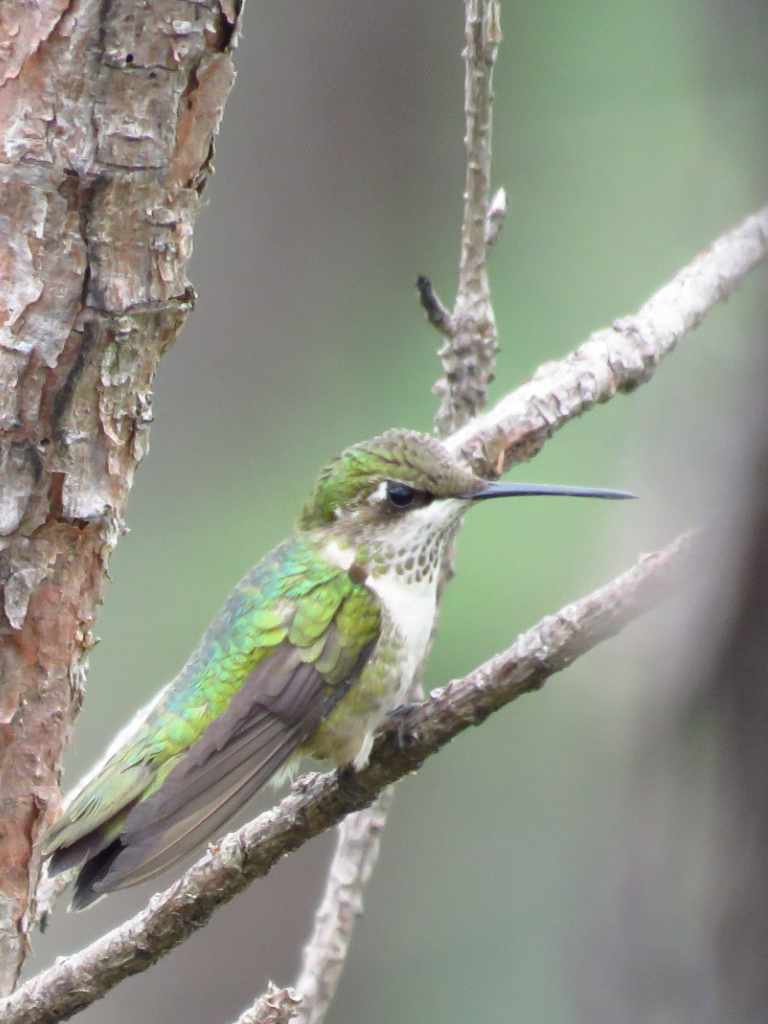
The Cinturón Verde demonstrated Eden’s expertise in managing diverse ecosystems critical to Honduras’ largest urban center. Highland cloud forests above 1,500 meters captured both rainfall and cloud moisture, while resilient pine-oak forests provided habitat for over 300 bird species, including the endangered Golden-cheeked Warbler and near-endemic Green-breasted Mountain Gem.
While the project is now inactive following Eden’s shift to carbon-eligible landscapes, its accomplishments in addressing key challenges – including a 16% loss of tree cover (2000-2022), severe pine bark beetle infestations affecting 14,000 hectares, and intense fire seasons – provide valuable lessons for future carbon projects. The advanced fire management systems developed here, including 1,200+ km of firebreaks and successful protection of 95% of restoration sites, demonstrate Eden’s capacity to ensure carbon permanence in fire-prone landscapes.

| Stat Label | Stat Value |
|---|---|
| Project Area | 96,500 hectares |
| Firebreaks Established | 107+ km of strategic firebreaks |

Community
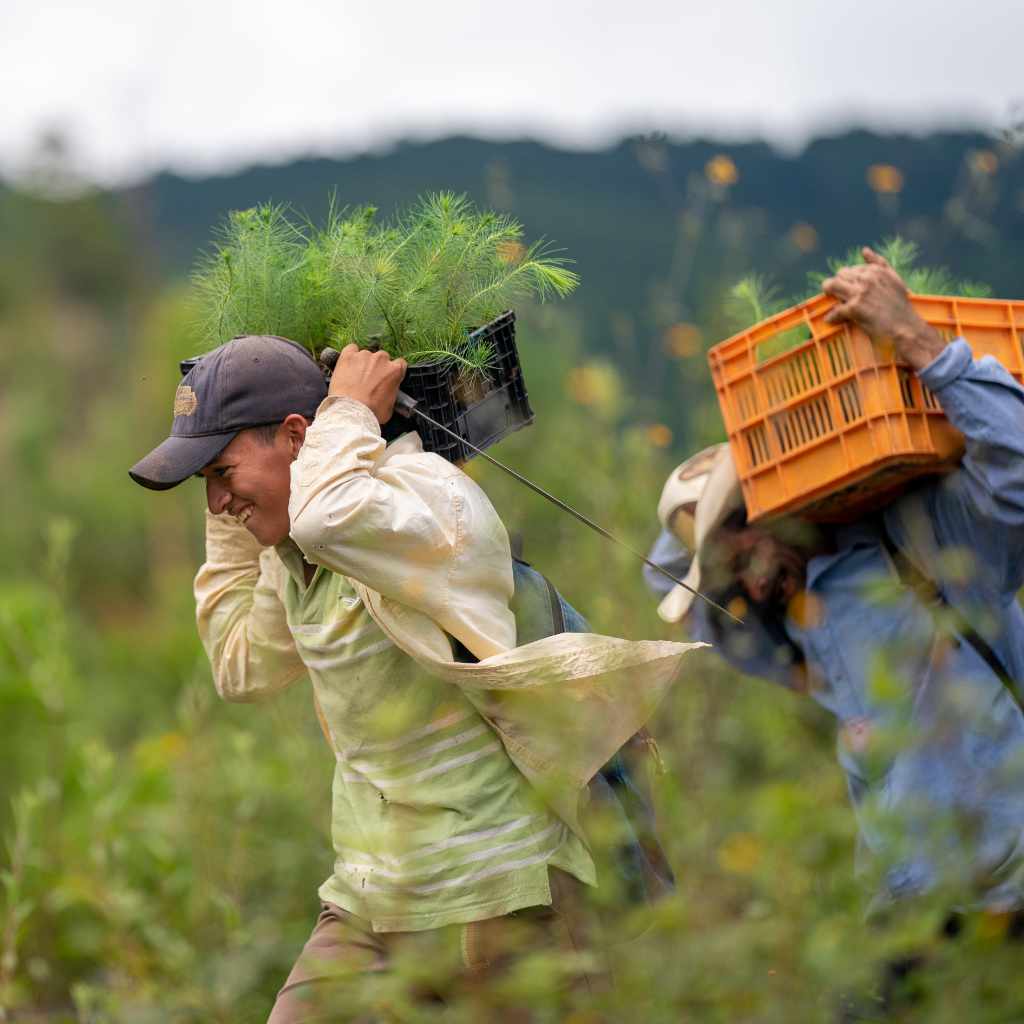
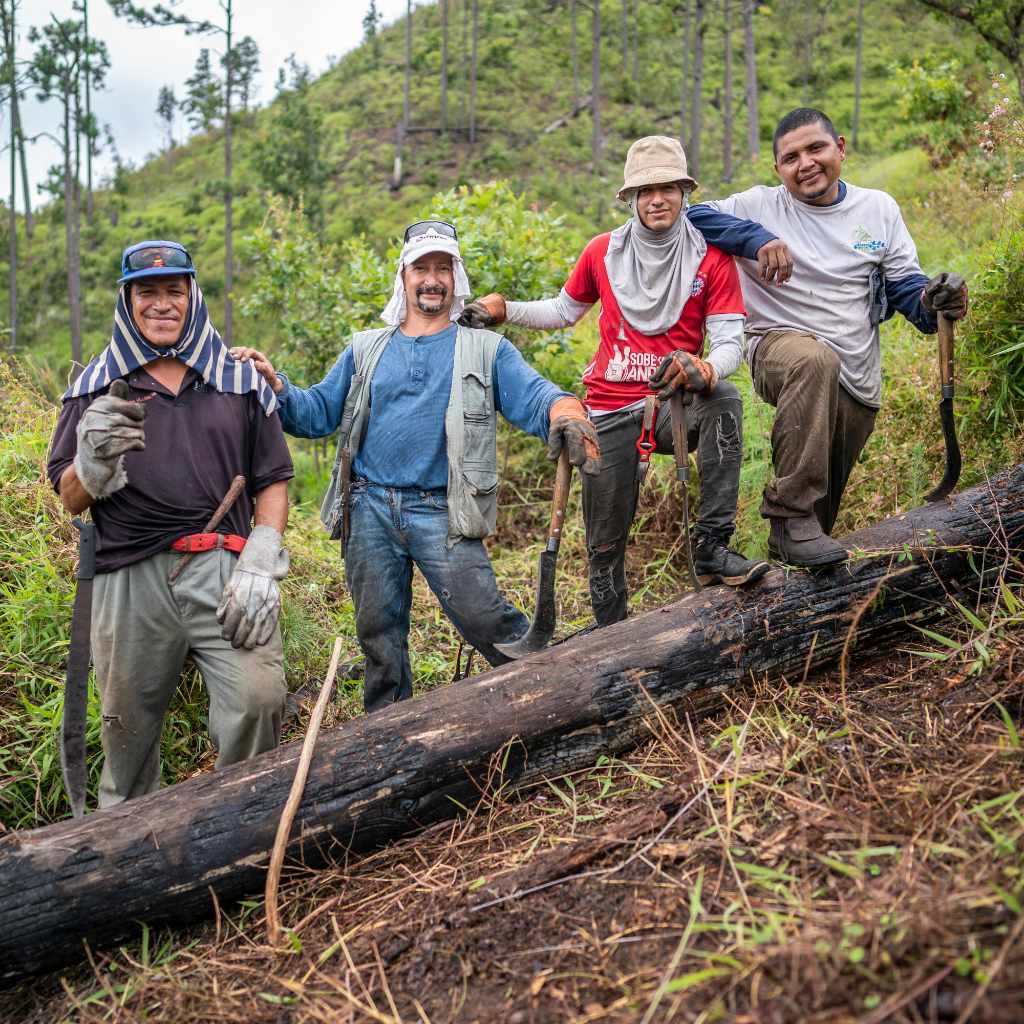
The communities surrounding Tegucigalpa demonstrated strong engagement in protecting the forested watersheds that sustained their water supply. Local water boards, municipal governments, and community organizations were essential partners in the Cinturón Verde restoration effort, contributing generational knowledge about landscape changes and fire management.
Through collaborative planning workshops, community members helped determine restoration strategies and participated in implementation through sustainable livelihood opportunities. The project’s emphasis on building local capacity for forest management and fire prevention created valuable expertise that now informs Eden’s carbon-eligible projects.
While inactive since 2024, the project’s dedication of 35% of its budget to sustainable livelihoods demonstrated how landscape restoration could foster community wellbeing while securing ecosystem services. These lessons continue to shape Eden’s approach to community engagement in carbon projects.
Technical Approach
The Cinturón Verde project demonstrated Eden’s expertise in landscape-scale fire management and watershed protection through its comprehensive technical approach. While now inactive due to strategic focus on carbon-eligible landscapes, its accomplishments provide valuable lessons for future carbon projects.
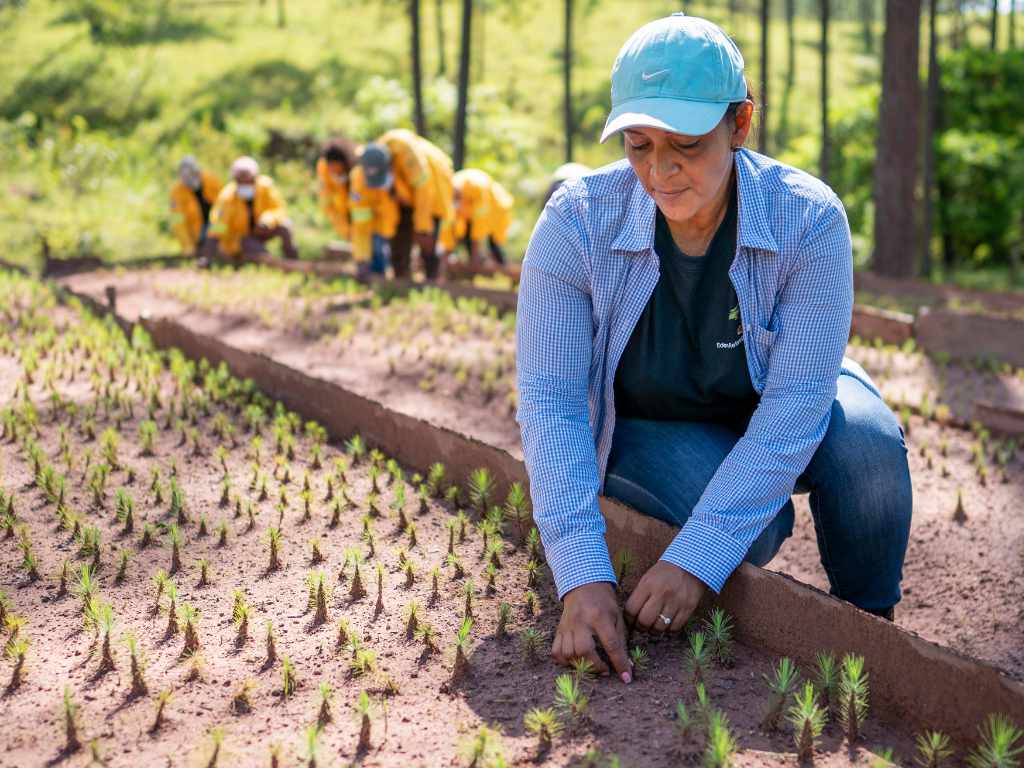
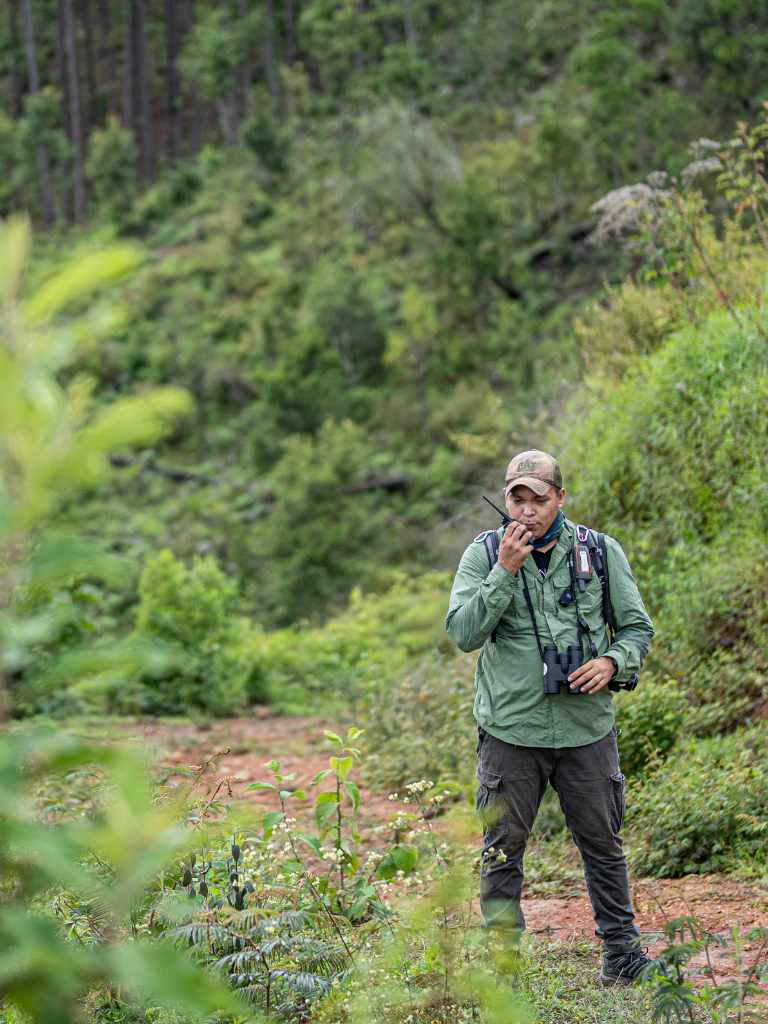
The project successfully implemented a two-phase geographic strategy prioritizing protected areas and corridors before expanding to watershed sub-basins. Key restoration techniques included assisted natural regeneration, indigenous species reforestation, and agroforestry systems. Notably, the project developed an advanced fire management system combining NASA FIRMS satellite monitoring with community response teams, resulting in 95% protection of restoration sites from uncontrolled fires.
Implementation occurred through coordinated partnerships with Instituto de Conservación Forestal, Cruz Verde Honduras, and local stakeholders. The project’s monitoring framework tracked forest cover change, fire incidents, water quality, and community engagement, generating expertise directly applicable to ensuring permanence in carbon-eligible landscapes.

Progress and Impact
The Cinturón Verde Restoration Project, while now inactive, achieved significant accomplishments that inform Eden’s current carbon-eligible work. The project team successfully developed an advanced fire management system that protected 95% of restoration sites, constructed over 1,200 km of strategic firebreaks, and established effective partnerships with Instituto de Conservación Forestal and Cruz Verde Honduras.
Key achievements included combating 154 forest fires, implementing NASA FIRMS monitoring systems, and developing multi-stakeholder response protocols that proved crucial during the severe 2024 fire season. These innovations in fire management and landscape protection demonstrate Eden’s capacity to implement complex restoration projects while providing valuable expertise for future carbon initiatives.
The project’s legacy of protecting critical water resources for Tegucigalpa through landscape restoration, combined with its successful fire management strategies, offers important lessons for ensuring carbon permanence and managing climate risks in Eden’s current portfolio of carbon-eligible projects.




